DuckDB / MotherDuck
Overview
DuckDB is an in-process SQL OLAP database management system designed for analytical workloads, aiming to be fast, reliable, and easy to integrate into data analysis applications. It supports standard SQL and operates directly on data in Pandas DataFrames, CSV files, and Parquet files, making it highly suitable for on-the-fly data analysis and machine learning projects. Rill supports natively connecting to and reading from a persisted DuckDB database that it has access to as a source by utilizing the DuckDB Go driver.
MotherDuck, on the other hand, is a managed DuckDB-in-the-cloud service, providing enhanced features for scalability, security, and collaboration within larger organizations. It offers advanced management tools, security features like access control and encryption, and support for concurrent access, enabling teams to leverage DuckDB's analytical capabilities at scale while ensuring data governance and security. Similarly, Rill supports natively connecting to and reading from MotherDuck as a source by utilizing the DuckDB Go driver.
Connecting to External DuckDB as a Source
As noted above, if you wish to connect to a persistent DuckDB database to read existing tables, Rill will first need to be able to access the underlying DuckDB database. Once access has been established, the data will be read from your external database into the built-in DuckDB database in Rill.
Local credentials
If creating a new DuckDB source from the UI, you should provide the appropriate path to the DuckDB database file under DB and use the appropriate DuckDB select statement to read in the table under SQL:
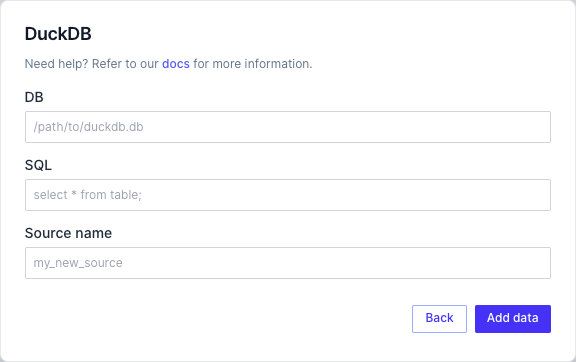
Alternatively, if you are creating the source YAML file directly, the definition should look something like:
type: "model"
connector: "duckdb"
sql: "SELECT * from <duckdb_table>"
db: "<path_to_duckdb_db_file>"
If you plan to deploy a project containing a DuckDB source to Rill Cloud, it is recommended that you move the DuckDB database file to a data folder in your Rill project home directory. You can then use the relative path of the db file in your source definition (e.g., data/test_duckdb.db).
Cloud deployment
Once a project with a DuckDB source has been deployed, Rill Cloud will need to be able to access and retrieve the underlying persisted database file. In most cases, this means that the corresponding DuckDB database file should be included within a directory in your Git repository, which will allow you to specify a relative path in your source definition (from the project root).
If the DuckDB database file is external to your Rill project directory, you will still be able to use the fully qualified path to read this DuckDB database locally using Rill Developer. However, when deployed to Rill Cloud, this source will throw an error.
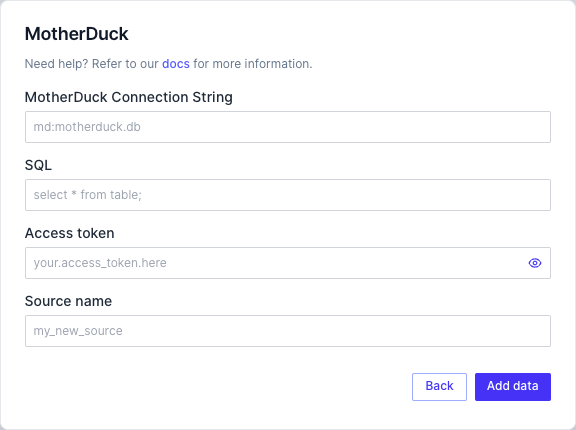
Connecting to MotherDuck
If you are creating the source YAML file directly, the definition should look something like:
type: "model"
connector: "motherduck"
sql: "SELECT * from <my_db>.<duckdb_table>"
db: "md:<my_db>"
Local credentials
When using Rill Developer on your local machine (i.e., rill start), Rill will use the motherduck_token configured in your environment variables to attempt to establish a connection with MotherDuck. If this is not defined, you will need to set this environment variable appropriately.
export motherduck_token='<token>'
An alternative option is to set this line in your bash profile.
For more information about authenticating with an appropriate service token, please refer to MotherDuck's documentation.
If this project has already been deployed to Rill Cloud and credentials have been set for this source, you can use rill env pull to pull these cloud credentials locally (into your local .env file). Please note that this may override any credentials you have set locally for this source.
Cloud deployment
Once a project with a MotherDuck source has been deployed, Rill requires you to explicitly provide the MotherDuck token using the following command:
rill env configure
Note that you must cd into the Git repository from which your project was deployed before running rill env configure.
If you've already configured credentials locally (in your <RILL_PROJECT_DIRECTORY>/.env file), you can use rill env push to push these credentials to your Rill Cloud project. This will allow other users to retrieve and reuse the same credentials automatically by running rill env pull.