3. Create the SQL Model
What is a model?
A data model in Rill is a used to perform intermediate processing as well as any last mile ETL on the source data required. We recommend creating "One Big Table" to power your metrics views.
Create a Model from the Source
Go ahead and select the Create Model button in the top right-hand corner from the commits dataset.
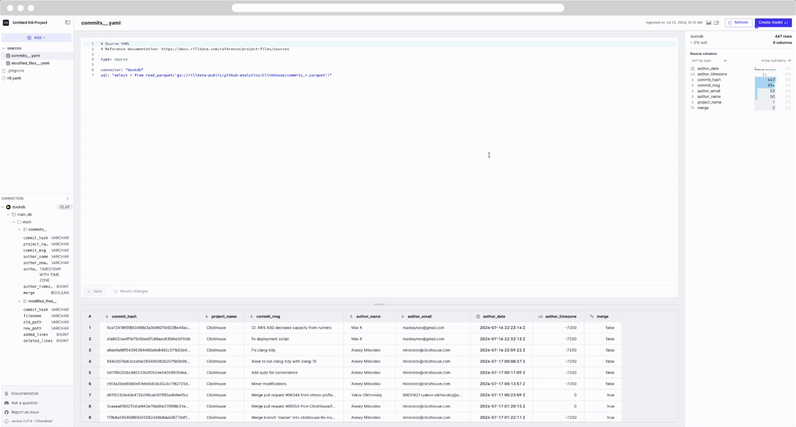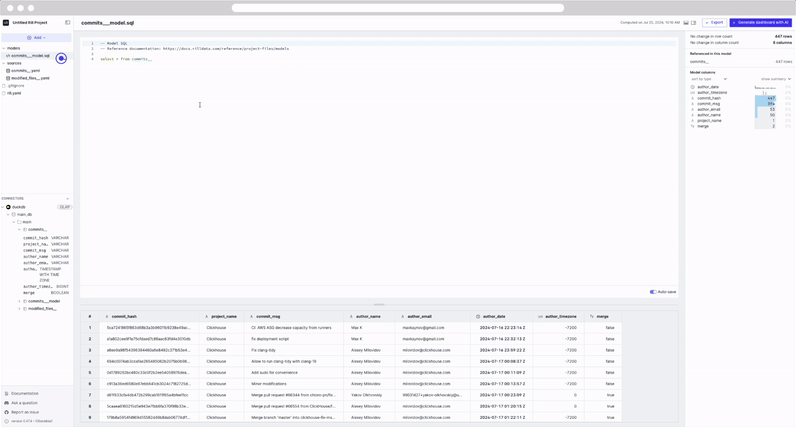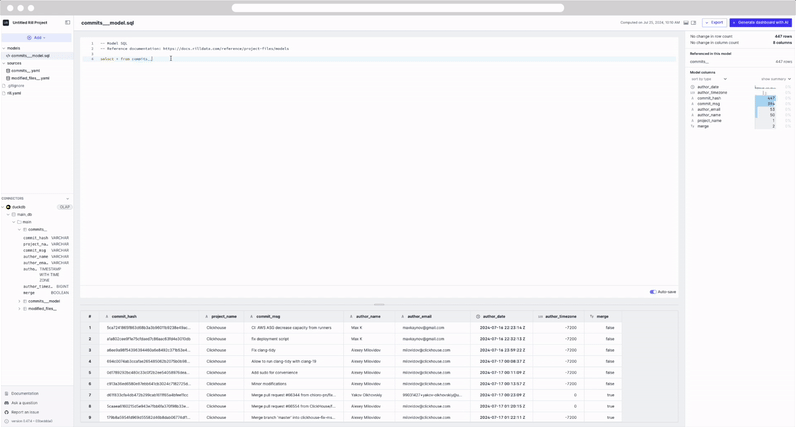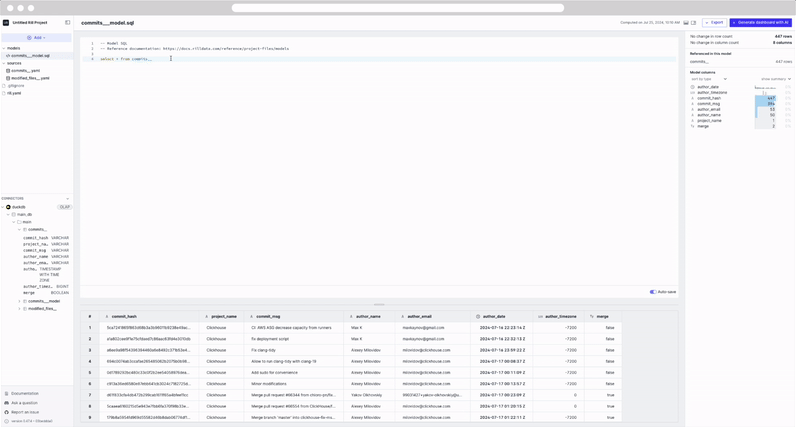
You'll be automatically redirected to the model page. On the left panel, you'll see a model's folder created with the file commits__model.sql. On the right panel, you'll find general information about your model table, the column values and at the bottom of the page, a preview of the data.
select * from commits
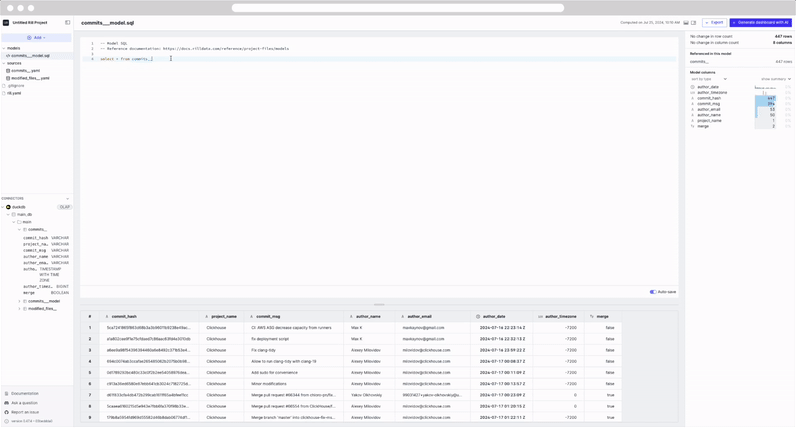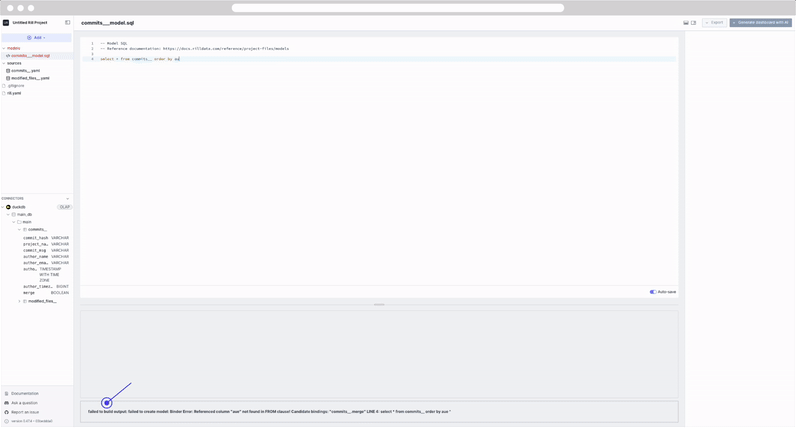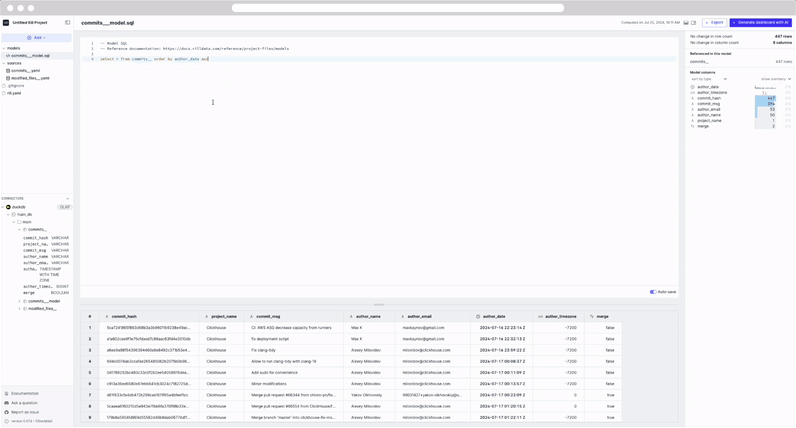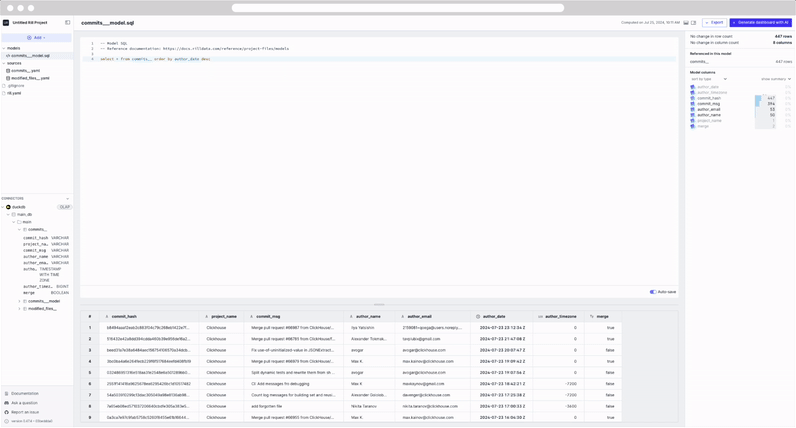
Let's try to make some changes to our SQL and see how the UI reacts.
select * from commits order by author_date DESC
Notice that the preview table is automatically updated as we modify the SQL. This is due to our auto-save feature. In case of any errors that are encountered the UI will update accordingly and display the error.
Our Autosave feature can be enabled/disabled as needed via the rill.yaml file / project settings, or by simply selecting the toggle in the UI.
Let's merge two tables!
Each dataset independently gives us some interesting information but we want to view the data from both of these datasets in a single dashboard.
- commits gives us information about the user who commited the changes.
- modified_files gives us information on the actual changes to the file and its directory.
We will grab all the columns from commits and only a few from modified_files as seen below. We will join the two datasets on the commit_hash column. As this is the SQL view that our dashboard will be based off of, we want to materialize it!
-- Model SQL
-- Reference documentation: https://docs.rilldata.com/reference/project-files/models
-- @materialize: true
SELECT
a.*,
b.filename,
b.added_lines,
b.deleted_lines
FROM
commits a
INNER JOIN
modified_files b
ON
a.commit_hash = b.commit_hash
You can see all referenced source tables in the right panel, as well as the column schema and an overview of the data. Select a model to be redirected to the model.
Concept: What is materialization?
By default, models created in DuckDB will be views. Both views and tables will be shown in under your DuckDB's connector table UI.
-- @materialize: true
Why materialize?
You may experience some improved performance materializing SQL views for intermediate models in the case of complex SQL or large data. We generally recommend materializing finals models that power dashboards. However, you might experience some degradation of modeling experience [auto-save feature] for some specific situations including cross joins.