Incremental Models
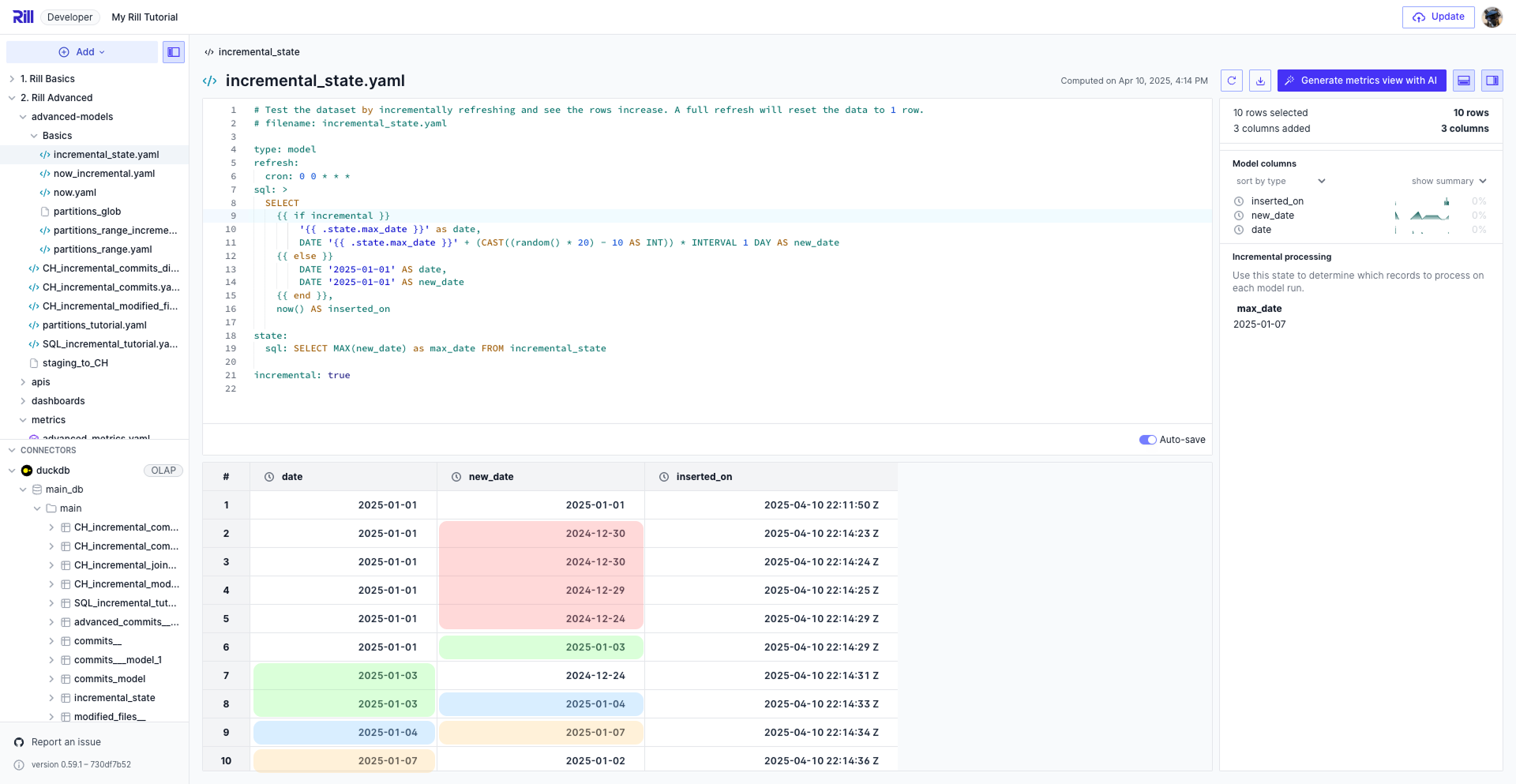
Before enabling incremental on the model, let's take a look at the following model YAML file, now.yaml. You'll notice that this is not our typical SQL model where we can write SQL statements into the textfile and have these automatically run. Instead, model YAML files requires a bit more setup such as defining the type: model, and the sql: parameter.
Getting Started
# This model outputs the current time every time it is refreshed.
type: model
sql: SELECT now() AS inserted_on
To understand what this is doing, let's go ahead and select the refresh button as seen in the screenshot below. This button performs the same command as the below in the CLI.
rill project refresh --model now --local
Since we're using Rill Developer, we will need to add the --local flag to the refresh commands or else this will refresh the project on Rill Cloud!
After the model refreshes, you should see the inserted_on value change.
Enable Increments on our Model
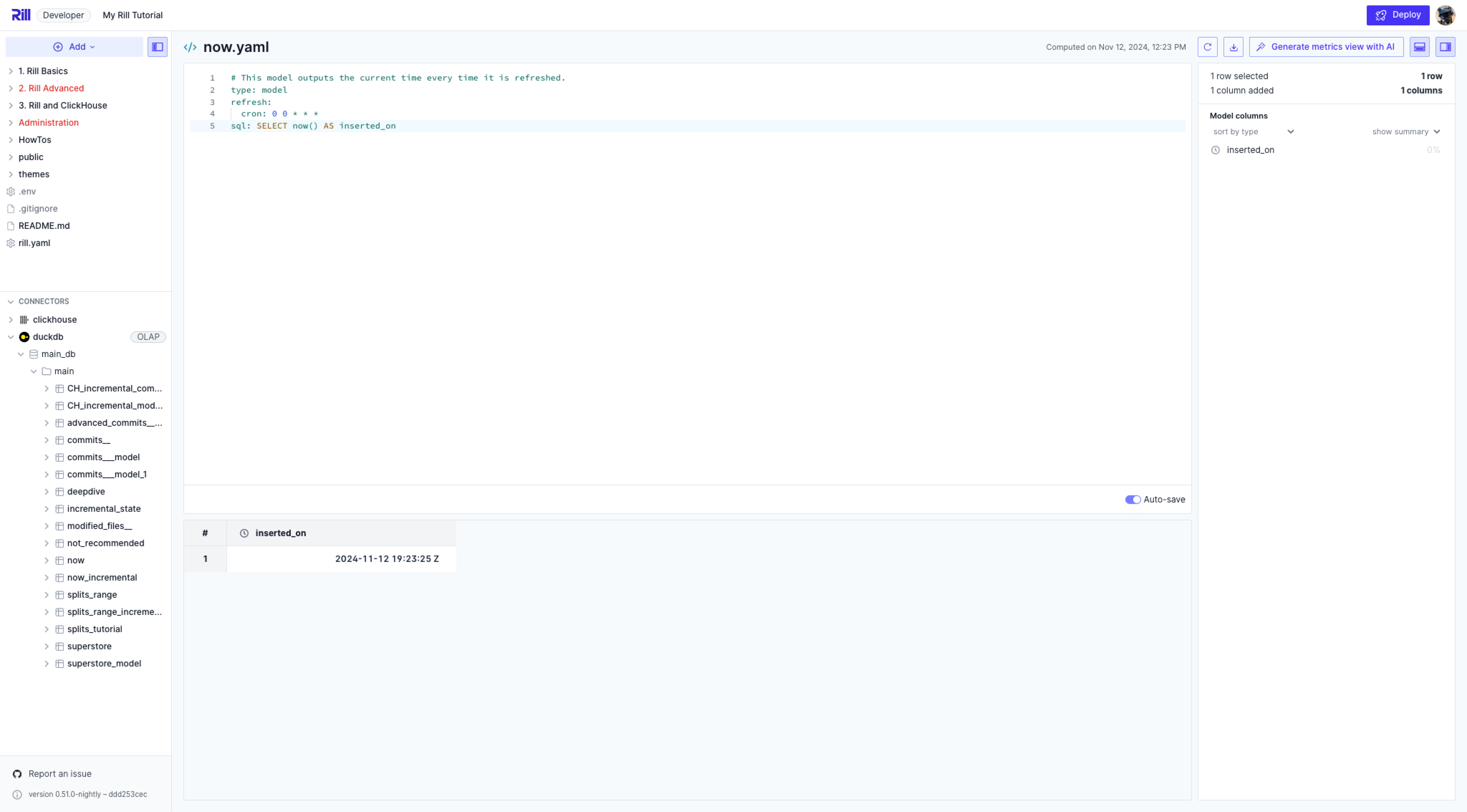
As mentioned previously, the incremental: true tells Rill that this model is an incremental model. You will see that the UI changes slightly when this is enabled. Not only will you be able to full refresh, but also incrementally refresh.
type: model
sql: SELECT now() AS inserted_on
incremental: true
When selecting the refresh button, a new drop down appears. In this case, we have the choice to incremental refresh or full refresh.
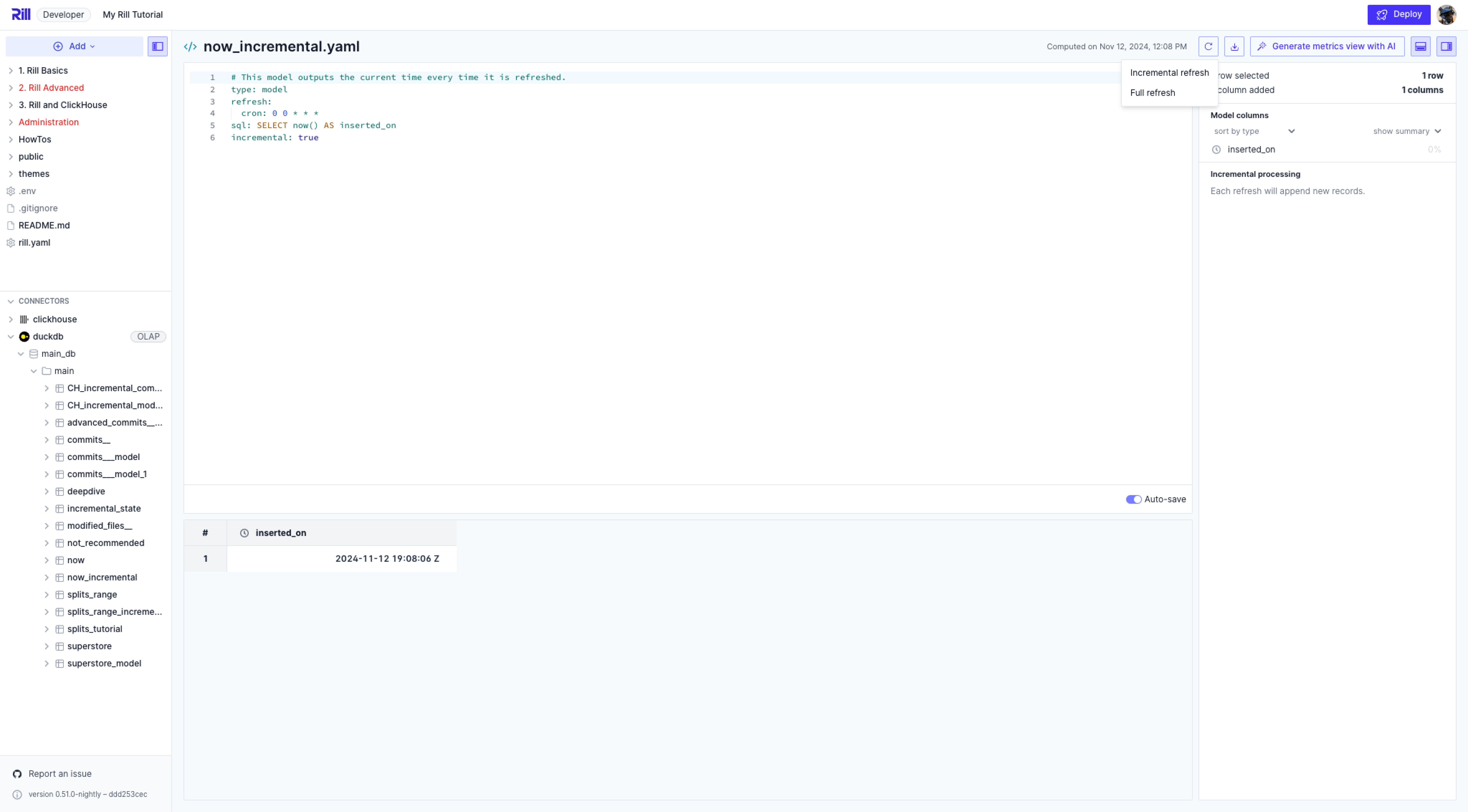
When you select Incremental Refresh, instead of overwriting the same row, we are now appending the new values of now() into the table.
Any changes to the model.yaml file will initiate a full refresh of the data. You can disable the auto-save feature to allow you some time to make all the needed changes before manually saving the file so as not to start multiple refreshes. Rill will be able to cancel a query if the file keeps changing.
Running the incremental refresh is the same as the following command in the CLI:
rill project refresh --model now_incremental --local
If you want to perform a full refresh you'll need to add the --full flag.
rill project refresh --model now_incremental --local --full
Next, let's take a moment to review states:.
States in Incremental Models
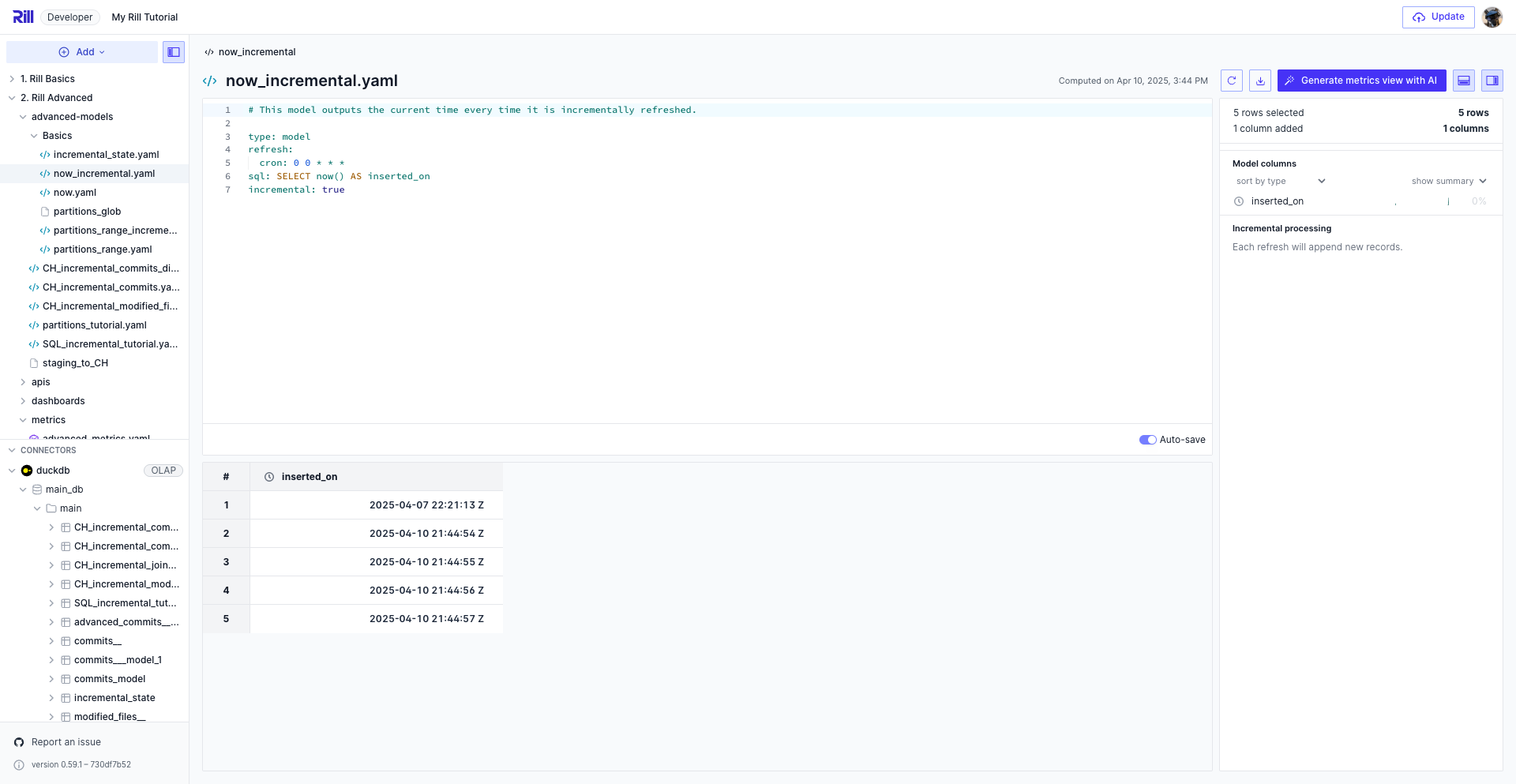
Next, we can add a state: key that allows us to manually define some sort of state in the model. In the following example, on a full refresh, we reset the date and new_date columns back to "2025-01-01". Each incremental refresh will run the query within {{if incremental}}, updating the column of date with max_date coming from our state query.
type:model
incremental: true
sql: >
SELECT
{{ if incremental }}
'{{ .state.max_date }}' as date,
DATE '{{ .state.max_date }}' + (CAST((random() * 20) - 10 AS INT)) * INTERVAL 1 DAY AS new_date
{{ else }}
DATE '2025-01-01' AS date,
DATE '2025-01-01' AS new_date
{{ end }},
now() AS inserted_on
state:
sql: SELECT MAX(new_date) as max_date FROM incremental_state
The following screenshot shows that for values of new_date that were smaller than the date, did not change the state but when new_date > date the following row was updated. This can be useful in states where the data is a timeseries dataset and you need to know to keep the max_date of your data. However, we will next discuss partitions which is a special state management system.